Current-Scaling a-Si:H TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for AM-OLEDs
Hojin Lee, Y. C. Lin, and Jerzy Kanicki
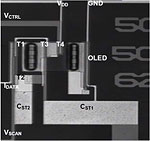 Today amorphous silicon thin-film transistor (a-Si:H TFT) active-matrix organic light-emitting displays (AM-OLEDs) emerge as very promising candidate for the next generation flat panel displays. In this project, we fabricated and characterized the a-Si:H TFT pixel electrode circuit with the current-scaling function that can be used for AM-OLEDs. The circuit consists of three switching TFTs (T1, T2, and T4), one driving TFT (T3), and two storage capacitors (CST1, CST2). This circuit showed an enhanced current-scaling performance for a high-resolution a-Si:H TFT AM-OLEDs in comparison to other types of current-driven pixel circuits. To evaluate the thermal and electrical stability of the fabricated pixel electrode circuits, we performed the Today amorphous silicon thin-film transistor (a-Si:H TFT) active-matrix organic light-emitting displays (AM-OLEDs) emerge as very promising candidate for the next generation flat panel displays. In this project, we fabricated and characterized the a-Si:H TFT pixel electrode circuit with the current-scaling function that can be used for AM-OLEDs. The circuit consists of three switching TFTs (T1, T2, and T4), one driving TFT (T3), and two storage capacitors (CST1, CST2). This circuit showed an enhanced current-scaling performance for a high-resolution a-Si:H TFT AM-OLEDs in comparison to other types of current-driven pixel circuits. To evaluate the thermal and electrical stability of the fabricated pixel electrode circuits, we performed the 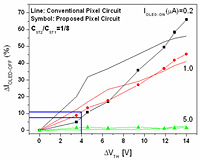 current temperature stress experiments. In general, this circuit showed a better electrical and thermal stability for different OLED current levels in comparison to the conventional current-driven pixel-electrode circuit. The long-term goal of this project is to implement these pixel circuit in future AM-OLED prototypes. This project was partially supported by the Research and Development Center of LG. Philips LCD, Korea. current temperature stress experiments. In general, this circuit showed a better electrical and thermal stability for different OLED current levels in comparison to the conventional current-driven pixel-electrode circuit. The long-term goal of this project is to implement these pixel circuit in future AM-OLED prototypes. This project was partially supported by the Research and Development Center of LG. Philips LCD, Korea.
H. Lee, Y.C. Lin, H.P.D. Shieh and J. Kanicki, IEEE Trans. Elec. Dev., 54, 2403, 2007.
top
|

