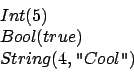Next: Class definitions
Up: Operational Semantics
Previous: Environment and the Store
Contents
Syntax for Cool Objects
Every Cool value is an object.
Objects contain a list of
named attributes, a bit like records in C. In addition, each object belongs to a class. We use
the following syntax for values in Cool:
Read the syntax as follows: The value 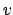 is a member of class
is a member of class 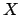 containing the attributes
containing the attributes
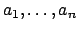 whose locations are
whose locations are
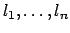 . Note that
the attributes have an associated location. Intuitively this means
that there is some space in memory reserved for each attribute.
The value
. Note that
the attributes have an associated location. Intuitively this means
that there is some space in memory reserved for each attribute.
The value 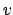 has dynamic type
has dynamic type 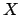 .
.
For base objects of Cool (i.e., Ints, Strings, and Bools) we use a
special case of the above syntax. Base objects have a class
name, but their attributes are not like attributes of normal
classes, because they cannot be modified. Therefore, we describe
base objects using the following syntax:
For Ints and Bools, the meaning is obvious. Strings contain two
parts, the length and the actual sequence of ASCII characters.




Next: Class definitions
Up: Operational Semantics
Previous: Environment and the Store
Contents